Write a Contract
In this guide we're going to create a simple smart contract that will allow us to store a string in the blockchain. This will teach you some of the basics of smart contract development on Vaulta.
Create your first Smart Contract
You can think of a Smart Contract like a function that runs on the blockchain. It must be deterministic, meaning that it will always produce the same output given the same input. This is required so that all nodes on the network can agree on the output of the function.
Open up the Vaulta Web IDE in your browser. You will be presented with a dummy contract which shows you the basic structure of a smart contract.
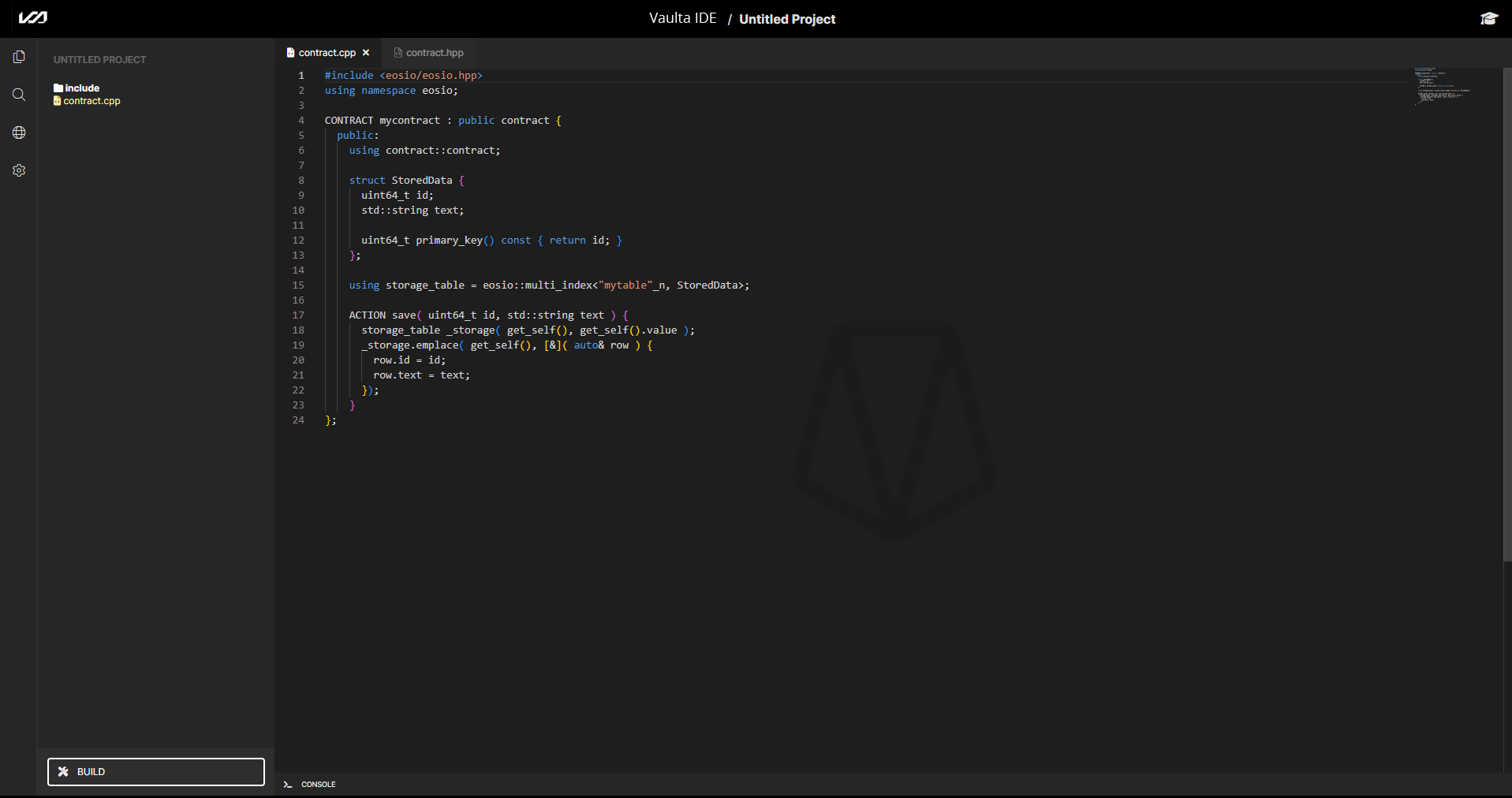
Go ahead and clear everything out of the editor, and copy and paste the following code:
#include <eosio/eosio.hpp>
using namespace eosio;
CONTRACT mycontract : public contract {
public:
using contract::contract;
TABLE StoredData {
uint64_t id;
std::string text;
uint64_t primary_key() const { return id; }
};
using storage_table = multi_index<"mytable"_n, StoredData>;
ACTION save( uint64_t id, std::string text ) {
storage_table _storage( get_self(), get_self().value );
_storage.emplace( get_self(), [&]( auto& row ) {
row.id = id;
row.text = text;
});
}
};
Take a look at the code and see if you can figure out what it's doing.
Here's the basic gist of it:
- You created a new contract called
mycontract - A table model called
StoredData - A table called
mytableto store yourStoredDatarecords - An action called
savethat will allow you to save a string to the table
If you're having trouble understanding the code, don't worry, you can head over to the Smart Contract Basics section to learn more about the various parts of a smart contract and how they work.
Your screen should look like this now:
Head over to the next section to see how we can deploy this to a testnet with a few clicks.