Contracts
There are a few different contracts involved in EOS staking.
eosio.system- The system and staking contract.eosio.reward- An intermediate reward dispersal contract.eosio.rex- Account that holds all funds in the staking protocol.
eosio.system
The system contract is wider than just staking and controls the entire EOS network with capabilities like account creation, chain governance, and resource management.
The staking portions of the system contract are responsible for managing the staking and unstaking of EOS tokens, as well as the distribution of rewards from the pre-allocated staking rewards pool.
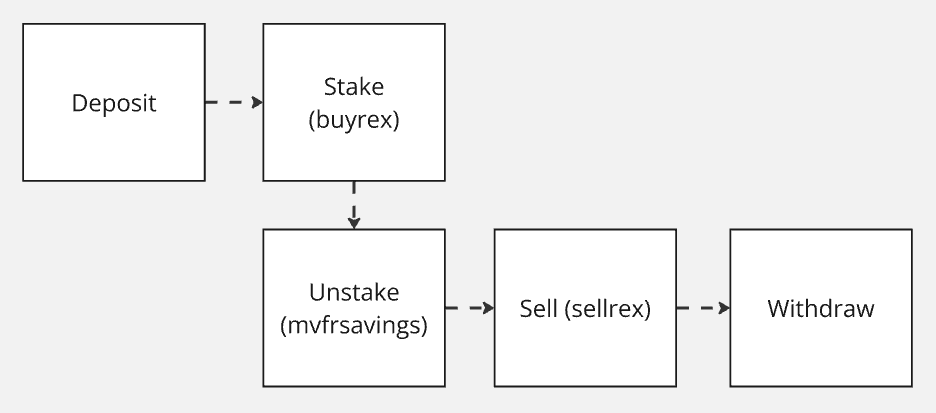
Depositing Funds
In order to use EOS inside the staking portion of the system contract, you need to deposit them first.
void deposit( const name& owner, const asset& amount )
This will transfer your funds to the eosio.rex account and register them as deposited into the staking protocol.
This will not stake them for you yet though, they are simply held within the protocol.
Parameters
The parameterowneris the account that is depositing the funds.
Staking Deposited Funds
Once you have deposited funds into the staking protocol, you can stake them to receive rewards.
void buyrex( const name& from, const asset& amount )
This will stake the funds that you have deposited into the staking protocol and issue you REX tokens in return.
Staking Funds From Voting Rights
On EOS you can have your EOS staked as voting rights. You may also use those funds as a source for staking.
void unstaketorex( const name& owner, const name& receiver, const asset& from_net, const asset& from_cpu )
This will move your voting rights staked funds into rewards staked funds, and issue you REX tokens in return. You will still retain your voting rights.
Note
All staked funds within the staking protocol have voting rights attached to them.
Unstaking Funds
void mvfrsavings( const name& owner, const asset& rex )
This will move funds out of eternally locked "savings" account and begin the 21 day unstaking period. Any funds you move out of that savings account within the same day will be attributed to the same unstaking bucket and mature within the same 21-day period.
Withdrawing Funds
Once the 21-day unstaking/maturation period has finished, you can sell your position and withdraw your funds. You will need to do this in two steps.
void sellrex( const name& from, const asset& rex )
This action will convert your REX tokens back into EOS and register them as available to withdraw.
void withdraw( const name& owner, const asset& amount )
This action will withdraw your EOS tokens from the staking protocol and transfer them to your account.
Note
Any action you take within the staking protocol once a 21-day unstaking period has finished will trigger an automaticsellrexon your fully matured REX tokens. This will convert them back into EOS and register them as available to withdraw.
Tables
The system contract has a few tables that are relevant to staking.
rexbal
The rexbal table holds information about staked balances for users.
versionownervote_stakerex_balance- the amount of REX ownedmatured_rex- matured REX available for sellingrex_maturities- An array of maturity dates and amounts
rexfund
The rexfund table
holds information about the deposited but unstaked EOS funds for users.
versionownerbalance- the amount of EOS deposited
rexmaturity
The rexmaturity table
holds information about the maturity dates of REX tokens for users.
num_of_maturity_buckets- The number of days until a position fully maturessell_matured_rex- A flag that indicates if to sell matured positions on any actionbuy_rex_to_savings- A flag that indicates if staked funds go directly to savings or not
rexpool
The rexpool table
holds information about the staking pool.
versiontotal_lent- total amount of EOS in open rex_loanstotal_unlent- total amount of EOS available to be lent (connector)total_rent- fees received in exchange for lent (connector)total_lendable- total amount of EOS that have been lent (total_unlent + total_lent)total_rex- total number of REX shares allocated to contributors to total_lendablenamebid_proceedsthe amount of EOS to be transferred from namebids to REX poolloan_numincrements with each new loan
This is useful if you want to calculate the price of EOS vs REX.
static convertEosToRex(eos:number){
const pool = get(rexpool);
if(!pool) return 0;
const S0 = parseFloat(pool.total_lendable.split(' ')[0]);
const S1 = S0 + eos;
const R0 = parseFloat(pool.total_rex.split(' ')[0]);
const R1 = (S1 * R0) / S0;
return parseFloat(parseFloat((R1 - R0).toString()).toFixed(4));
}
static convertRexToEos(rex:number){
const pool = get(rexpool);
if(!pool) return 0;
const S0 = parseFloat(pool.total_lendable.split(' ')[0]);
const R0 = parseFloat(pool.total_rex.split(' ')[0]);
const R1 = R0 + rex;
const S1 = (S0 * R1) / R0;
return parseFloat(parseFloat((S1 - S0).toString()).toFixed(4));
}
If you'd like to view full code for this example, see here.
rexretpool
The rexretpool table
holds information about the return pool for REX tokens.
versionlast_dist_time- the last time proceeds from renting, ram fees, and name bids were added to the rex poolpending_bucket_time- timestamp of the pending 12-hour return bucketoldest_bucket_time- cached timestamp of the oldest 12-hour return bucketpending_bucket_proceedsproceeds in the pending 12-hour return bucket,current_rate_of_increasethe current rate per dist_interval at which proceeds are added to the rex pool,proceedsthe maximum amount of proceeds that can be added to the rex pool at any given time
eosio.reward
The reward contract (see contract code) is an intermediate contract that is responsible for dispersing the rewards from the staking rewards tokenomics bucket to the various strategies aimed at rewarding the EOS community.
It allows the EOS Network to define a set of receivers that will receive rewards, and a weight for each receiver.
See the inflows document for more information on how the reward contract is funded.
Note
Modifying strategies is controlled by the block producers and requires a 15/21 multisig to change.
Adding or Updating Strategies
void setstrategy( const name strategy, const uint16_t weight )
This action will set or update a strategy with a given weight. The weight is a percentage of the total rewards that will be allocated to this strategy. For instance, if there are three strategies with weights of 1000, 2000, and 7000, then the first strategy will receive 10% of the rewards, the second 20%, and the third 70%.
Removing Strategies
void delstrategy( const name strategy )
This will remove any strategy from the reward contract.
Distributing Rewards
void distribute()
Funds that have flowed into this contract since the last distribution will be distributed to the strategies based on their weights. It is better to call this at a higher interval to make sure that any small amounts of funds are not lost to rounding errors.
Note
Any account can call this action.
eosio.rex
The contract on the eosio.rex account is merely a record-keeping contract. Each of the actions
does nothing (no implmentation) and is only there to provide an identifiable record within the transactions stack that
can be tracked and filtered by external tooling such as history solutions or frontend SDKs that want more
information that normally would not be available (like the REX received for an amount of EOS in a buyrex action).
void buyresult( const asset& rex_received ) { }
void sellresult( const asset& proceeds ) { }
void orderresult( const name& owner, const asset& proceeds ) { }
void rentresult( const asset& rented_tokens ) { }
As different actions trigger results on the eosio.rex account, it will add one of these identifiable records to the
transaction stack based on the calling action. For instance, if you call buyrex, you will see a buyresult record.